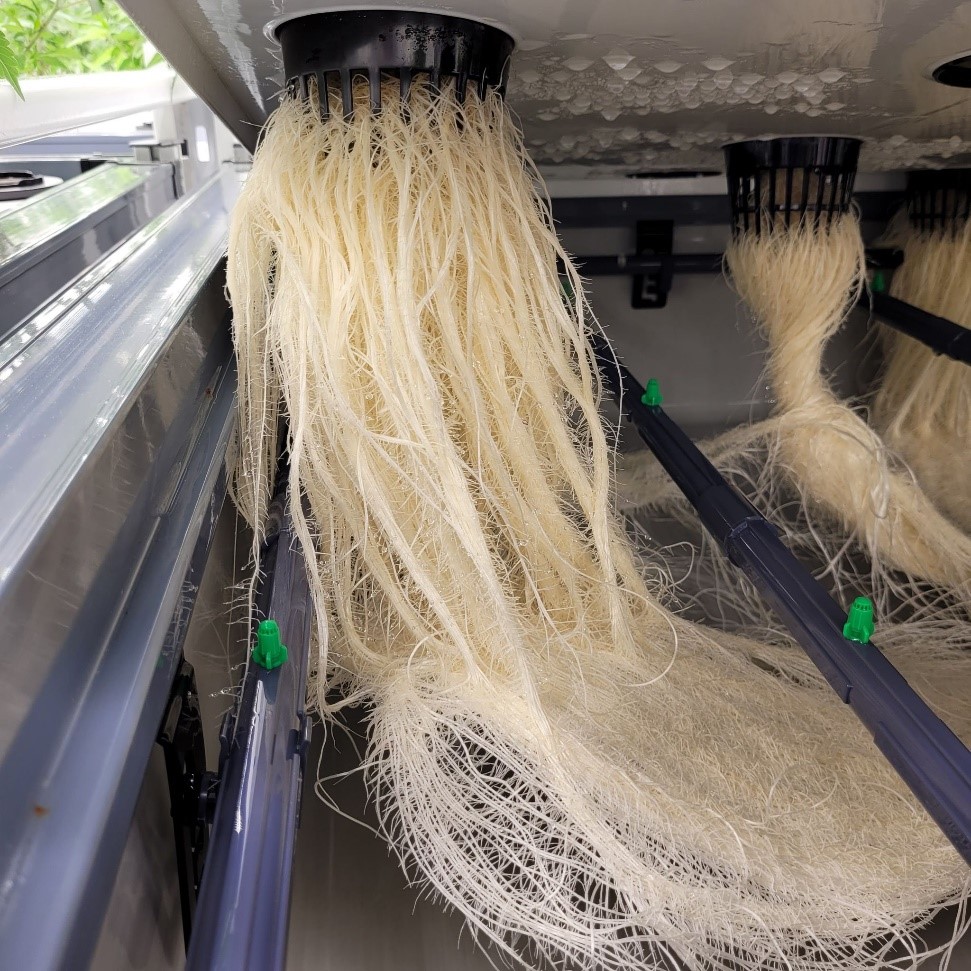
For its cannabis cultivation, SUMO has chosen aeroponics: a soilless culture where roots develop in the open air inside a spray chamber. However, did you know that there are other different techniques to grow cannabis? This article will explain a little more about each of them.
Aeroponics
Aeroponics involves strategically spraying the root area with pH balanced water and measured nutrient solutions. This improves the growth rate of the roots, thus improving the overall growth rate of the plants. This technique has many advantages, as shown in the article: What is aeroponics? This technique allows a deep rinsing of the roots at the end of the flowering cycle of the plant, which offers a purer taste and a whiter smoke during consumption.
Open ground culture
Open ground culture is certainly the most well-known of all. The main advantage of this technique is that the nutrients go directly into the soil. It is possible to add certain elements, but in general, the necessary nutrients are already present in the soil. All the producer has to do is add water. However, this technique requires a lot of handling and cleaning by employees.
Hydroponics
Hydroponics means simply growing plants in water. The plants are placed in growing media such as coconut fibre or rockwool, and then fed a nutrient solution to make them grow. Since many hydroponic methods employ some type of growing medium these methods are often termed “soilless culture”, while water culture alone is true hydroponics.1 With this technique, the cannabis producer must balance the pH and make sure to add water and nutrients.
Aquaponics
Aquaponics is a method that combines the cultivation of plants and fish breeding. In this instance, it consists of growing cannabis plants in an aquatic environment, without inert support. This method also incorporates fish, which inhabit a basin under the plants. Nutrients come directly from the water, in connection with the positive effects of the presence and activity of fish.
There are also three main types of environments for producing cannabis:
Outside (field)
Producing cannabis in an outdoor environment has its challenges, especially in Canada, with the changing seasons. This shortens the period suitable for cultivation, because of pollination, freezing of the soil, etc. Animals and other outdoor parasites can also interfere with production. This will ultimately affect the quality of the product, since only about one harvest per year is possible in this scenario. However, it is the most natural and least expensive way to grow cannabis.
Greenhouse
Greenhouse cultivation is usually carried out in large production areas. Lighting is usually provided by sunlight, but growers must regularly compensate with artificial lighting on cloudy days or days where the sun rises late and sets early. Therefore, producers using this environment are still dependent on climate and seasons. Since greenhouses are usually less well hermetic than buildings, they may be less impervious to environmental influences and odor emission into the neighborhood.
Indoor (building)
Cultivation in an indoor building, like SUMO Cannabis, allows a better control of the environment (humidity, heat, light, etc.) and of the whole production process. Furthermore, since the production rooms are independent of each other, if a problem occurs with one batch, the rest of the production is not affected. This environment also offers better odor control, especially outside the building. SUMO Cannabis chose this production setting for its various advantages, including the fact that it allows for the year-round cultivation of quality cannabis.
1 https://agriculture.canada.ca/en/news-agriculture-and-agri-food-canada/scientific-achievements-agriculture/what-hydroponics